When Mumbai-based rubber component manufacturer Precision Seals was struggling with mounting scrap rates that were eating into their profits, they knew something had to change. Their aging mixing and kneading equipment wasn’t just inefficient—it was costing them nearly ₹2.5 lakhs per month in wasted material.
Fast forward six months after upgrading their rubber processing machinery, and the results speak for themselves: a 30% reduction in scrap, improved batch consistency, and a payback period of just 14 months.
This rubber scrap reduction case study reveals exactly how they did it—and how your plant can achieve similar results.
The Problem: Hidden Costs of Outdated Mixing Equipment
Precision Seals had been operating with the same rubber mixing mill and kneader for over 15 years. While the machines still ran, the problems were mounting:
High Scrap Rates: Their monthly scrap rate hovered around 8-10% of total rubber compound processed. For a plant processing 25 tons monthly, that meant wasting 2-2.5 tons of valuable material.
Inconsistent Batches: Temperature variations during mixing led to under-mixed or over-mixed batches. Quality control rejected roughly 12% of finished compounds, which had to be reprocessed or scrapped entirely.
Extended Mixing Times: What should have taken 8-10 minutes per batch was stretching to 15-18 minutes due to worn rollers and inadequate temperature control.
Frequent Downtime: The old equipment required repairs every 3-4 weeks, disrupting production schedules and adding maintenance costs.
As production manager Rajesh Kumar explained: “We knew our equipment was the bottleneck, but we didn’t realize how much it was actually costing us until we calculated the real numbers. The scrap waste alone was shocking.”
The Analysis: Identifying Root Causes
Before investing in new equipment, Precision Seals conducted a thorough process audit with their machinery supplier, Vikas Industries. The analysis revealed several critical issues:
1. Temperature Control Problems
The existing mixing mill lacked precision temperature monitoring. Rubber compounds are temperature-sensitive—too hot and you risk scorching; too cold and you get inadequate dispersion. Their old system couldn’t maintain the ±3°C accuracy needed for consistent results.
2. Inadequate Kneading Intensity
The dispersion kneader was undersized for their current production volume. The mixing chamber couldn’t generate sufficient shear force to properly disperse fillers like carbon black and silica, leading to weak spots in the final compound.
3. Worn Roller Surfaces
After 15 years of operation, the mixing mill rollers had developed uneven wear patterns. This created inconsistent nip gaps, resulting in poor blend homogeneity and higher reject rates.
4. Manual Process Controls
Most parameters—temperature, mixing time, and pressure—were manually controlled. Human error and inconsistent operator practices contributed significantly to batch variation.
According to research from the Rubber Manufacturers Association, outdated mixing processes account for up to 40% of quality-related scrap in small to mid-sized rubber plants—a statistic that matched Precision Seals’ experience perfectly.
The Solution: Strategic Equipment Upgrade
Based on the audit findings, Precision Seals implemented a targeted upgrade strategy focusing on their core mixing and kneading operations.
Phase 1: New Dispersion Kneader Installation
They installed a modern Dispersion Kneader with the following improvements:
- Increased Chamber Volume: Upgraded from 35L to 55L capacity to handle larger batches more efficiently
- Enhanced Mixing Blades: New rotor design with optimized blade geometry for better dispersion
- Automated Temperature Control: PLC-based system maintaining ±2°C accuracy
- Pressure Monitoring: Real-time pressure sensors ensuring consistent mixing intensity
Phase 2: Rubber Mixing Mill Modernization
Within 60 days, they replaced their primary Rubber Mixing Mill with a two-roll mill featuring:
- Precision Roller Grinding: Factory-calibrated rollers with microfinish surface quality
- Variable Speed Control: Independent motor drives for each roller, allowing optimal speed ratios
- Digital Temperature Display: Accurate monitoring across the entire roller length
- Emergency Stop Systems: Enhanced safety features protecting both operators and equipment
Phase 3: Process Standardization
The new equipment enabled them to:
- Create standard operating procedures (SOPs) for each compound recipe
- Implement automated batch logging and traceability
- Establish quality checkpoints at mixing, kneading, and extrusion stages
- Train operators on optimal machine utilization
The total investment came to approximately ₹35 lakhs, including installation, training, and process optimization support.
The Results: Measurable Impact on Scrap Reduction
Three months after full implementation, the improvements were dramatic:
Key Performance Metrics (Before vs. After)
Scrap Rate:
- Before: 8-10% average
- After: 5.5-6.5% average
- Improvement: 30% reduction in scrap waste
Batch Consistency:
- Before: 88% first-pass acceptance rate
- After: 96% first-pass acceptance rate
- Improvement: 9% increase in quality acceptance
Mixing Time per Batch:
- Before: 15-18 minutes average
- After: 9-12 minutes average
- Improvement: 35% reduction in cycle time
Monthly Scrap Value:
- Before: ₹2.5 lakhs in wasted material
- After: ₹1.75 lakhs in wasted material
- Savings: ₹75,000 per month (₹9 lakhs annually)
Maintenance Downtime:
- Before: 48-60 hours monthly
- After: 12-15 hours monthly
- Improvement: 75% reduction in unplanned downtime
Return on Investment
With monthly savings of ₹75,000 from reduced scrap alone (not counting improved throughput and reduced downtime), Precision Seals calculated a payback period of just 14 months on their ₹35 lakh investment.
“The ROI was faster than we expected,” said Rajesh Kumar. “Between the scrap savings, increased capacity, and reduced maintenance costs, this investment paid for itself in little over a year. We wish we’d done it sooner.”
Key Lessons: What Made This Mixing Optimization Successful
1. Data-Driven Decision Making
Precision Seals didn’t just replace equipment blindly. They measured current performance, identified specific bottlenecks, and selected machinery that addressed their exact needs.
2. Comprehensive Operator Training
New equipment only delivers results when operators understand how to use it properly. They invested in 40 hours of hands-on training for their mixing and kneading team.
3. Process Documentation
Standardized recipes and SOPs eliminated the “tribal knowledge” problem where results depended on which operator was running the shift.
4. Preventive Maintenance Schedule
Rather than running equipment until it failed, they implemented a preventive maintenance program that catches issues before they cause downtime or quality problems.
5. Continuous Monitoring
They established daily quality checks and weekly performance reviews to catch any deviations early and maintain the improvements.
The Rubber Division of the American Chemical Society emphasizes that process optimization must combine equipment upgrades with systematic operational improvements—exactly the approach Precision Seals took.
Applying These Lessons to Your Rubber Processing Operation
If you’re experiencing similar challenges with scrap rates, batch inconsistency, or aging equipment, here’s a practical roadmap:
Step 1: Calculate Your True Scrap Cost
Track scrap rates for 30 days across all processes. Don’t just count obvious rejects—include:
- Trimming waste from hot feed extruders or cold feed systems
- Off-spec batches requiring rework
- Material lost during color or compound changes
- Edge trim from compression molding on rubber hydraulic presses
Step 2: Identify Your Biggest Loss Points
Where in your process does scrap occur most frequently? For many plants, it’s during:
- Mixing and kneading (poor dispersion)
- Sheet formation (thickness variation)
- Extrusion (die swell inconsistency)
- Molding (flash, short shots, contamination)
Step 3: Evaluate Equipment Condition
Honestly assess your current machinery:
- How old is your primary mixing and kneading equipment?
- What’s the maintenance history?
- Are you experiencing declining first-pass quality rates?
- Can your equipment handle your current volume efficiently?
Step 4: Create an Upgrade Priority List
You may not need to replace everything at once. Focus on:
- Equipment causing the most scrap
- Bottleneck processes limiting throughput
- Safety-critical machinery
- Equipment with highest maintenance costs
Step 5: Partner with Experienced Manufacturers
Work with established rubber machinery manufacturers who understand process optimization, not just equipment sales. Look for suppliers who offer:
- Process audits and consultations
- Customization for your specific compounds
- Comprehensive training programs
- After-sales technical support
- Spare parts availability
Contact Vikas Industries for a free process assessment to identify your scrap reduction opportunities.
Beyond Mixing: Other Equipment That Impacts Scrap Rates
While Precision Seals focused on mixing and kneading, several other equipment categories significantly impact overall scrap rates:
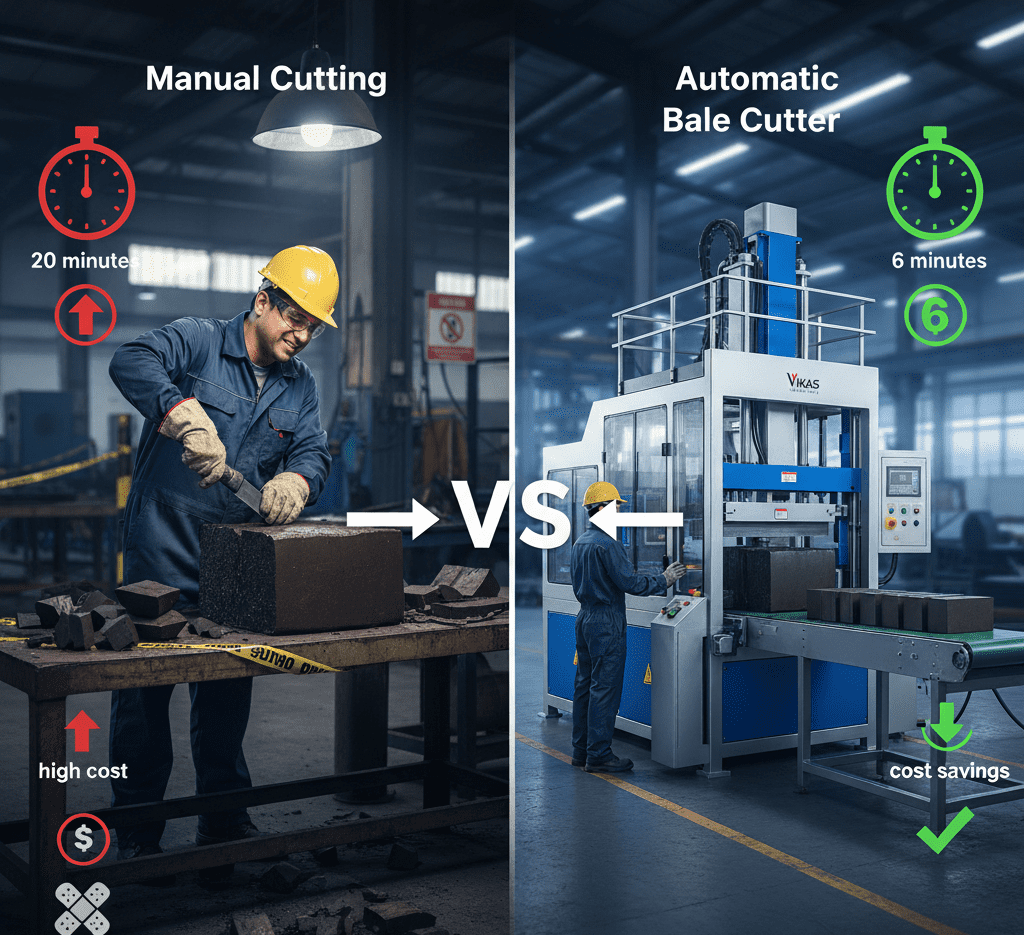
Rubber Bale Cutters
Proper material preparation starts with consistent bale cutting. Modern rubber bale cutters ensure uniform piece sizes, which improve feeding consistency into mills and kneaders, reducing mixing time variation.
Hot Feed & Cold Feed Extruders
Extrusion is another common scrap source. Upgrading to precision extruders with better die temperature control and consistent feeding mechanisms can reduce profile variation and edge trim waste.
Hydraulic Presses
For molded goods production, modern rubber hydraulic presses with programmable pressure curves and precise temperature zones minimize flash and ensure complete cavity fill—two major sources of molding scrap.
The Bigger Picture: Sustainability and Competitiveness
Reducing scrap isn’t just about cost savings—it’s increasingly important for:
Environmental Responsibility: Less waste means lower environmental impact and better alignment with sustainability goals.
Regulatory Compliance: Many industries now require suppliers to document waste reduction efforts.
Competitive Advantage: Lower scrap rates allow you to quote more competitive prices while maintaining healthy margins.
Customer Confidence: Demonstrating consistent quality and process control strengthens customer relationships and opens doors to quality-sensitive markets.
Taking the First Step Toward Scrap Reduction
Precision Seals’ success story demonstrates that significant improvements are achievable with the right combination of modern equipment, process discipline, and operator training.
Whether your scrap rate is 5% or 15%, there’s almost certainly room for improvement. The first step is understanding where your losses occur and what’s causing them.
Ready to reduce your rubber processing scrap rates?
- Explore our complete range of rubber processing machinery
- Read our guide: 5 Signs Your Rubber Mixing Mill Needs Replacement (related blog post)
- Learn more about: Kneader Process Optimization Best Practices (related blog post)
- Schedule a free process audit: Request a consultation
Vikas Industries has helped dozens of rubber plants across India optimize their processing operations. From mixing mills to complete production lines, we provide machinery designed for reliability, precision, and measurable ROI.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the typical scrap rate for rubber mixing processes?
Industry benchmarks suggest well-optimized rubber mixing operations maintain scrap rates between 3-6%. Plants with older equipment or less process control often see 8-12% scrap rates. Anything above 10% indicates significant opportunity for process improvement and equipment modernization.
How long does it take to see ROI from new rubber processing equipment?
ROI timelines vary based on current scrap rates, production volume, and equipment cost. Most plants see payback periods between 12-24 months when factoring in scrap reduction, increased throughput, and reduced maintenance. Higher volume operations often achieve even faster returns.
Can I reduce scrap without replacing equipment?
Yes, partial improvements are possible through better process controls, operator training, and preventive maintenance. However, severely worn or undersized equipment has physical limitations that only replacement can address. A process audit can identify which improvements are possible with existing equipment.
What’s the difference between a mixing mill and a dispersion kneader?
A rubber mixing mill uses two counter-rotating rollers to blend compounds through shearing action—ideal for mastication and final mixing. A dispersion kneader uses rotating blades in an enclosed chamber to intensively mix compounds with fillers—better for initial dispersion. Most plants need both for complete processing.
How do I calculate my actual scrap costs?
Calculate total scrap costs by tracking: (1) Raw material value of scrapped compounds, (2) Labor cost for producing rejected batches, (3) Energy consumed in failed production, (4) Disposal costs for unusable scrap, and (5) Opportunity cost of capacity used for rejected product. Many plants find true costs are 40-60% higher than material costs alone.
What maintenance extends rubber processing equipment life?
Key maintenance includes: daily roller cleaning and inspection, weekly lubrication of bearings and gears, monthly alignment checks, quarterly temperature calibration, and annual comprehensive inspection. Modern equipment with condition monitoring systems can predict maintenance needs before failures occur, preventing costly downtime.